Common Log File Locations
Error logs are very important for the diagnosis and troubleshooting ofproblems with applications. Depending on the operating system and application type, the location of these log files can vary.
Linux/Unix Systems
- /var/log/: This directory is the primary location for storing log files on Linux systems. Common log files include:
- syslog: General system logs1.
- auth.log: Authentication logs.
- dmesg: Kernel ring buffer logs.
- apache/error.log: Apache web server error logs.
- Service-Specific Logs: Most services maintain their logs in
/var/log/. For example:- MySQL:
/var/log/mysql/error.log1. - Nginx:
/var/log/nginx/error.log.
- MySQL:
- Application Logs: Applications might store logs in:
/var/log/<application_name>/./opt/<application_name>/logs/.~/.<application_name>/logs/.
Windows Systems
- Event Viewer: Windows logs significant events in the Event Viewer.
- Application Logs: Accessible via Event Viewer > Windows Logs > Application.
- Application-Specific Logs: Applications might store logs in:
C:\ProgramData\<application_name>\logs\C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\<application_name>\logs\.
Specific File Names
Applications may use standard naming conventions. However, it’s common to find logs such as error.log, application.log, debug.log, or app.log within the locations mentioned above.
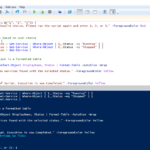
Viewing Error Logs Using SSH
Accessing error logs via SSH allows administrators to monitor and troubleshoot issues remotely2. Here are some common commands to view these logs:
Common Commands and Switches
1. cat Command
- Syntax:
cat <filename> - Description: Used to display the content of a file.
- Example:
cat /var/log/syslog.
2. tail Command
- Syntax:
tail [options] <filename>. - Options:
-n <number>: Displays the lastnlines1. Example:tail -n 10 /var/log/nginx/error.log1.-f: Follows the log, displaying new entries in real-time1. Example:tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log1.
3. less Command
- Syntax:
less <filename> - Description: Allows for paginated viewing of files, making it easier to scroll through large logs.
- Example:
less /var/log/mysql/error.log.
4. grep Command
- Syntax:
grep [options] <pattern> <filename>. - Options:
-i: Case-insensitive search2.-v: Inverts the search, displaying lines that do not match the pattern.
- Example:
grep -i "error" /var/log/apache2/error.log.
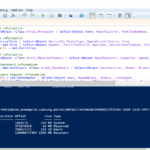
5. journalctl Command (Systemd Systems)
--since and --until: Filters logs within a specific time range.
Example: `journalctl -u ssh –since “2024-07-01” –until “2024-07-12″[1].
Syntax: journalctl [options]
Options:
-u <service>: Filters logs for a specific service. Example: journalctl -u ssh.
Display last 100 lines of the Apache error log
tail -n 100 /var/log/apache/error.log